Page 1570 - MISUMI SINGAPORE Economy Series
P. 1570
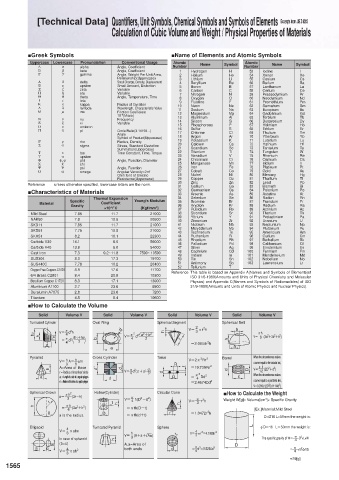
[Technical Data] Quantifiers, Unit Symbols, Chemical Symbols and Symbols of Elements Excerpts from JIS Z 8202
Calculation of Cubic Volume and Weight / Physical Properties of Materials
■Greek Symbols ■Name of Elements and Atomic Symbols
Uppercase Lowercase Pronunciation Conventional Usage Atomic Name Symbol Atomic Name Symbol
alpha Angle, Coefficient Number Number
beta Angle, Coefficient 1 Hydrogen H 53 Iodine I
gamma Angle, Weight Per Unit Area, 2 Helium He 54 Xenon Xe
Relationship(Uppercase) 3 Lithium Li 55 Cesium Cs
delta Small Change, Density, Displacement 4 Beryllium Be 56 Barium Ba
epsilon Small Amount, Distortion 5 Boron B 57 Lanthanum La
zeta Variable 6 Carbon C 58 Cerium Ce
eta Variable 7 Nitrogen N 59 Praseodymium Pr
theta Angle, Temperature, Time 8 Oxygen O 60 Neodymium Nd
iota 9 Fluorine F 61 Promethium Pm
kappa Radius of Gyration 10 Neon Ne 62 Samarium Sm
lambda Wavelength, Characteristic Value 11 Sodium Na 63 Europium Eu
mu Friction Coefficient 12 Magnesium Mg 64 Gadolinium Gd
10 -6 (Micro)
nu Frequency 13 Aluminum Al 65 Terbium Tb
66
Dy
Si
Dysprosium
14
Silicon
xi Variable
omicron 15 Phosphorous P S 67 Holmium Ho
Erbium
16
Sulfur
Er
68
pi Circle Ratio(3.14159...) 17 Chlorine Cl 69 Thulium Tm
Angle
Symbol of Product(Uppercase) 18 Argon Ar 70 Ytterbium Yb
rho Radius, Density 19 Potassium K 71 Lutetium Lu
sigma Stress, Standard Deviation 20 Calcium Ca 72 Hafnium Hf
Summation(Uppercase) 21 Scandium Sc 73 Tantalum Ta
tau Time Constant, Time, Torque 22 Titanium Ti 74 Tungsten W
upsilon 23 Vanadium V 75 Rhenium Re
phi Angle, Function, Diameter 24 Chromium Cr 76 Osmium Os
chi 25 Manganese Mn 77 Iridium Ir
psi Angle, Function 26 Iron Fe 78 Platinum Pt
omega Angular Verocity=2πf 27 Cobalt Co 79 Gold Au
Ohm:Unit of Electric 28 Nickel Ni 80 Mercury Hg
Resistance(Uppercase) 29 Copper Cu 81 Thallium Tl
Reference unless otherwise specified, lowercase letters are the norm. 30 Zinc Zn 82 Lead Pb
Gallium
Bismuth
Ga
83
31
Bi
■Characteristics of Materials 32 Germanium Ge 84 Polonium Po
As
85
Astatine
33
At
Arsenic
Thermal Expansion 34 Selenium Se 86 Radon Rn
Specific Young's Modulus 35 Bromine Br 87 Francium Fr
Material Gravity Coefficient 36 Krypton Kr 88 Radium Ra
×10 -6 /˚C {Kgf/mm 2 } 37 Rubidium Rb 89 Actinium Ac
Mild Steel 7.85 11.7 21000 38 Strontium Sr 90 Thorium Th
NAK80 7.8 12.5 20500 39 Yttrium Y Zr 91 Protactinium Pa
U
Uranium
Zirconium
92
40
SKD11 7.85 11.7 21000 41 Niobium Nb 93 Neptunium Np
SKD61 7.75 10.8 21000 42 Molybdenum Mo 94 Plutonium Pu
Americium
Am
Tc
95
Technetium
43
SKH51 8.2 10.1 22300 44 Ruthenium R 96 Curium Cm
Carbide V30 14.1 6.0 56000 45 Rhodium Rh 97 Berkelium Bk
Palladium
Pd
98
46
Cf
Californium
Carbide V40 13.9 6.0 54000 47 Silver Ag 99 Einsteinium Es
Cast Iron 7.3 9.2~11.8 7500~ 10500 48 Cadmium Cd 100 Fermium Fm
Md
In
101
Indium
Mendelevium
49
SUS304 8.0 17.3 19700 50 Tin Sn 102 Nobelium No
SUS440C 7.78 10.2 20400 51 Antimony Sb 103 Lawrencium Lr
52
T
Tellurium
Oxygen Free Coppers C1020 8.9 17.6 11700 Reference This table is based on Appendix A(Names and Symbols of Elements)of
6/4 Brass C2801 8.4 20.8 10300 ISO 31/8-1980(Amounts and Units of Physical Chemistry and Molecular
Beryllium Copper C1720 8.3 17.1 13000 Physics) and Appendix C(Names and Symbols of Radionuclides) of ISO
Aluminum A1100 2.7 23.6 6900 31/9-1980(Amounts and Units of Atomic Physics and Nuclear Physics).
Duralumin A7075 2.8 23.6 7200
Titanium 4.5 8.4 10600
■How to Calculate the Volume
Solid Volume V Solid Volume V Solid Volume V Solid Volume V
Turncated Cylinder Oval Ring Spherical Segment Spherical Belt
2
Q 2 d h V= 2 3 Qr h b
d h
Qh
h2 h h1 V= 4 h1+h2 V= Q 2 d 2 a 2 +b 2 V= 6 (3a +3b +h ) 2
2
2
d (
= Q 2 2 ) b 4 2 r 2 h
4
d =2.0944r h a
a
Pyramid Cross Cylinder Torus V=2Q Rr 2 Barrel When the circumference makes
2
V= h A= h arn R a curve equal to the circular arc,
6
3
A=Area of Base R , r =19.739Rr 2 QR 2 2
d
h d V= d (R+R ’ - ) d D V= 12 (2D +d )
Q 2
r=Radius of inscribed circle 4 3 d
a a=Length of a side of a regular polygon R D = Q 2 Dd 2 R When the circumference makes
4
n=Number of the sides of a regular polygon =2.4674Dd 2 a curve equal to a parabolic line,
2
V=0.209R(2D Dd+1/4d ) 2
Spherical Crown Qh 2 Hollow(Cylinder) Circular Cone ■How to Calculate the Weight
a= 3 (3r-h) Q h(D -d )
2
2
r h
r d t V= 4 V= Q 2 Weight W[g]= Volume[cm 3 ]× Specific Gravity
3
h = Qh (3a +h ) 2 h =Qth(D-t) h [Ex.]Material:Mild Steel
2
6
a D r =1.0472r h
2
a is the radius. =Qth(d+t) D=Ø16 L=50mm the weight is:
Ellipsoid 4 Turncated Pyramid Sphere L FD=16 L=50mm the weight is:
4
V= 3 Qabc h r V= Qr =4.1888r 3
3
3
2
In case of spheroid h V= 3 (A+a+ Aa) The specific gravity of W = Q 4 D ×L×W
(b=c) A.a=Area of D
a c b 4 2 both ends d = d =0.5236d 3 = Q ×1.6 ×5×7.85
Q 3
2
V= 3 Qab 6 4
≈79[g]
1565 1566