Page 1583 - MISUMI SINGAPORE Economy Series
P. 1583
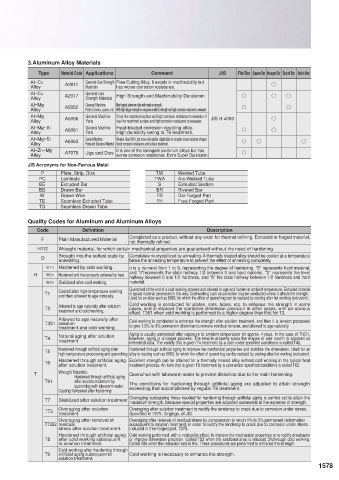
3.Aluminum Alloy Materials
Type Material Code Applications Comment JIS Flat Bar Square Bar Hexagonal Bar Round Bar Section Steel
Al−Cu A2011 General-Use Strength Free-Cutting Alloy. It excels in machinability but
Alloy Materials has worse corrosion resistance. k
Al−Cu General-Use
Alloy A2017 Strength Materials High Strength and Machinability Duralumin k k k
Al−M General Machine Most typical aluminum alloy with medium strength.
Alloy A5052 Parts Covers, cases, etc. With high fatigue strength in comparison with its strength and high corrosion resistance to seawater. k k
Al−M A5056 General Machine It has fine machined surface and high corrosion resistance to seawater. It JIS H 4000 k
Alloy Parts has fine machined surface and high corrosion resistance to seawater.
Al−M −Si A6061 General Machine Heat-treated corrosion resisting alloy.
Alloy Parts High durability owing to T6 treatment. k k
Al−M −Si General Machine Weaker than 6061, but more extrudable. Applicable to complex cross-sections shapes.
Alloy A6063 Parts and Structural Material Good corrosion resistance and surface treatment. k k k
Al−Zn−M It is one of the strongest aluminum alloys but has
Alloy A7075 Jigs and Dies worse corrosion resistance. Extra Super Duralumin k
JIS Acronyms for Non-Ferrous Metal
P Plate, Strip, Disk TW Welded Tube
PC Laminate TWA Arc-Welded Tube
BE Extruded Bar S Extruded Section
BD Drawn Bar BR Riveted Bar
W Drawn Wire FD Die-Forged Part
TE Seamless Extruded Tube FH Free-Forged Part
TD Seamless Drawn Tube
Quality Codes for Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys
Code Definition Description
F Plain Manufactured Material Completed as a product, without any order for thermal refining. Extruded or forged material,
not thermally refined.
H112 Wrought material, for which certain mechanical properties are guaranteed without the need of hardening.
O Brought into the softest state by Completely re-crystallized by annealing. A thermally treated alloy should be cooled at a temperature
below the annealing temperature to prevent the effect of annealing completely.
annealing.
H1n Hardened by cold working. n is a numeral from 1 to 9, representing the degree of hardening. "8" represents hard material,
H H2n Hardened and then properly softened by heat. and "4"represents the state halfway 1/2 between 0 and hard material. "2" represents the level
halfway between 0 and 1/2 hardness, and "6" the state halfway between 1/2 hardness and hard
H3n Stabilized after cold working. material.
Cooled after high-temperature working Quenched at the end of a cold working process and allowed to age and harden at ambient temperature. Extruded material
T1 and then allowed to age naturally. is typical material processed in this way. Cold working such as correction may be conducted unless it affects the strength.
Used for an alloy such as 6063, for which the effect of quenching can be realized by cooling after hot working (extrusion).
T3 Allowed to age naturally after solution Cold working is conducted for plates, rods, tubes, etc. to enhance the strength in some
cases, and to improve the corrective dimension precision in other cases, with an obvious
treatment and cold working.
effect. T361 when cold working is performed to a higher degree than that for T3.
Allowed to age naturally after Cold working is conducted to enhance the strength after solution treatment, and then it is tension processed
T351 solution to give 1.5% to 3% permanent distortion to remove residual tension, and allowed to age naturally.
treatment and cold working.
Natural aging after solution Aging is usually completed after exposure to ambient temperature for approx. 4 days. In the case of 7NO1,
T4 treatment however, aging is a longer process. The tensile property upon the elapse of one month is adopted as
referential data. The variety that is given T4 treatment by a user under specified conditions is called T42.
T5 Hardened through artificial aging after Hardened through artificial aging to improve the mechanical properties and stabilize the dimensions. Used for an
high-temperature processing and quenching alloy or casting such as 6063, for which the effect of quenching can be realized by cooling after hot working (extrusion).
T6 Hardened through artificial aging Excellent strength can be attained for a thermally treated alloy without cold working in the typical heat
after solution treatment.
treatment process. An item that is given T6 treatment by a user under specified conditions is called T62.
T Wrought Materials: Quenched with lukewarm water to prevent distortion due to the main hardening.
Hardened through artificial aging
T61 after solution treatment by The conditions for hardening through artificial aging are adjusted to attain strength
quenching with lukewarm water. exceeding that accomplished by regular T6 treatment.
Casting:Tempered after hardening
T7 Stabilized after solution treatment Overaging surpassing those needed for hardening through artificial aging is carried out to attain the
maximum strength, because special properties are adjusted somewhat at the expense of strength.
T73 Overaging after solution Overaging after solution treatment to rectify the tendency to crack due to corrosion under stress.
Specified in 7075, forgings, of JIS.
treatment.
Overaging after removal of Overaging after removal of residual stress by compression to retain 1% to 5% permanent deformation
T7352 residual subsequent to solution treatment, in order to rectify the tendency to crack due to corrosion under stress.
stress after solution treatment. Included in free-forged part, 7075.
Hardened through artificial aging Cold working performed, with a noticeable effect, to improve the mechanical properties or to rectify drawbacks
T8 after cold working subsequent or improve dimension precision. Called T83 when the sectional area is reduced 3%through cold working.
to solution treatment. Called T86 when the reduction rate is 6%. These procedures are performed to enhance the strength.
Cold working after hardening through
T9 artificial aging subsequent to Cold working is necessary to enhance the strength.
solution treatment.
1577 1578